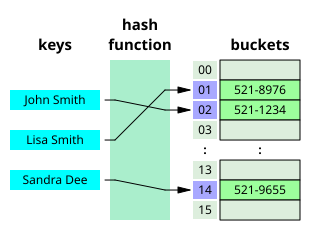
- You look up a word (key) and get its definition (value)
- You don’t go page by page — you jump directly to the word, thanks to indexing (like hashing)
 The main advantage of hash maps is their average O(1) time complexity for these operations, meaning the time it takes doesn’t grow with the number of elements.
Implementing Dictionaries in Programming Languages: In Python, the
The main advantage of hash maps is their average O(1) time complexity for these operations, meaning the time it takes doesn’t grow with the number of elements.
Implementing Dictionaries in Programming Languages: In Python, the dict data type is a highly optimized hash map implementation. Other languages like Java, C++, and JavaScript also have built-in hash map structures (HashMap, unordered_map, and Object/Map respectively).
Storing Unique Values: Hash maps can be used to efficiently store unique elements, as each key in a hash map must be unique. This makes them useful for tasks like removing duplicate items from a list.
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Fast Lookup | O(1) average time to access data by key |
| Flexible Keys | Keys can be strings, numbers, or tuples (Keys must be unique) |
| Dynamic Size | Grows as needed |
| Built-in Support | Available in almost all languages (e.g., dict in Python, Map in JavaScript, HashMap in Java) |
Use Cases
- Fast Data Lookups: Hash maps are ideal for situations where you need to retrieve a value based on a specific key very quickly. For example, a phone book application where you want to find a person’s number using their name, or a user database where you want to retrieve a user’s profile using their username.
- Counting Frequencies: You can use a hash map to count the occurrences of items in a list. The item itself becomes the key, and its count becomes the value. For instance, counting the frequency of each word in a document.

